Import
CSV Data Onto a Map
In this guide we’ll show you how to create a new map and import a CSV.
We’ll use a sample CSV file for practice, containing files with both location data and no
location data.
Time to complete: 5 mins.
Contents
1. Getting started
1.1 Download sample files
1.2 Create a new map
2. Upload your data
3. Configuring your imports
3.1 Setting your coordinate system (EPSG)
3.2 Configuration
1. Getting started
1.1. Download sample files
Sample files to download: Sample CSV
The zip file contains 2 CSV files - one with spatial information
(location data) and one without.
1.2. Create a new map
Click on MAPS section and select
CREATE MAP.
This will open up the first page of the
map creation wizard.
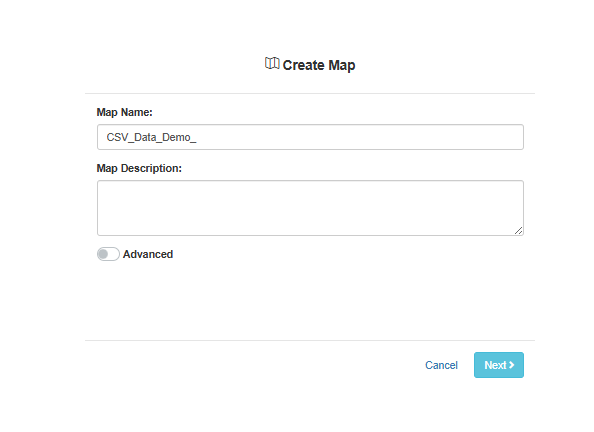
Name your new map and select NEXT.
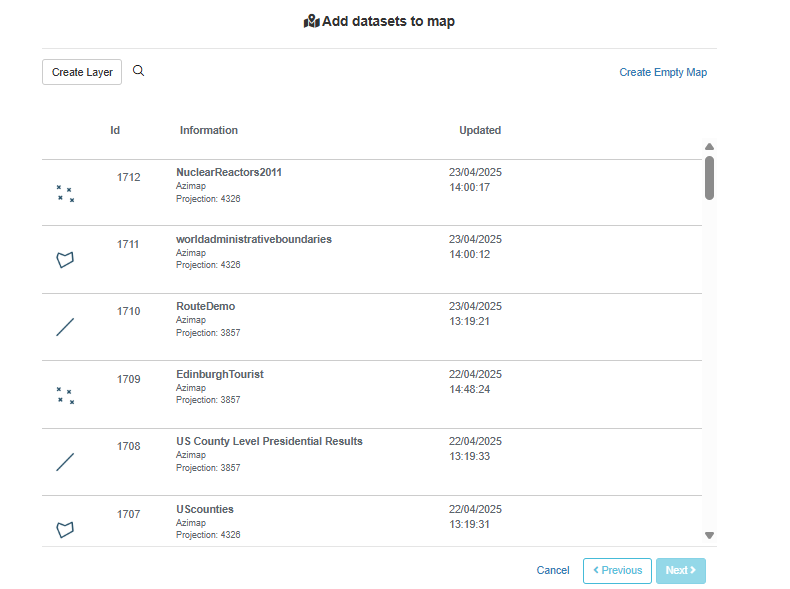
2. Import data and add to map
At this stage you have a number of
options. You can create a brand new layer for your map by selecting the CREATE
LAYER button. Alternatively you can choose to upload one or many of your
existing layers onto your map (your full list of layers will appear), or you
choose to create an empty map.
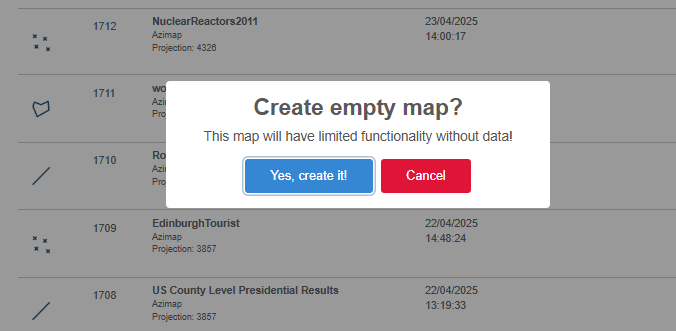
When you try to load a map without
any layers attached you will get the below warning.
In this case however, we'll choose
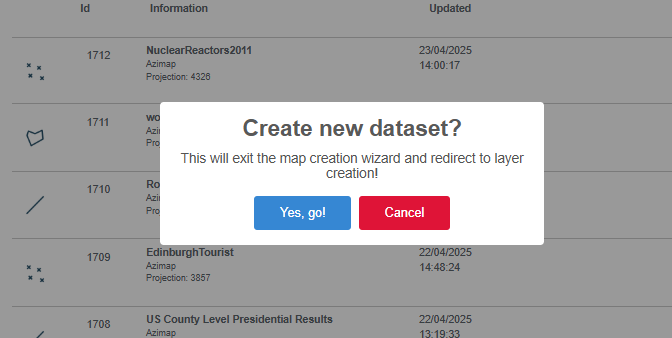
the CREATE LAYER button (this is also accessible on the map using the gears
button on the layer tree view). You'll be prompted with the below
pop-up. Select YES, GO.
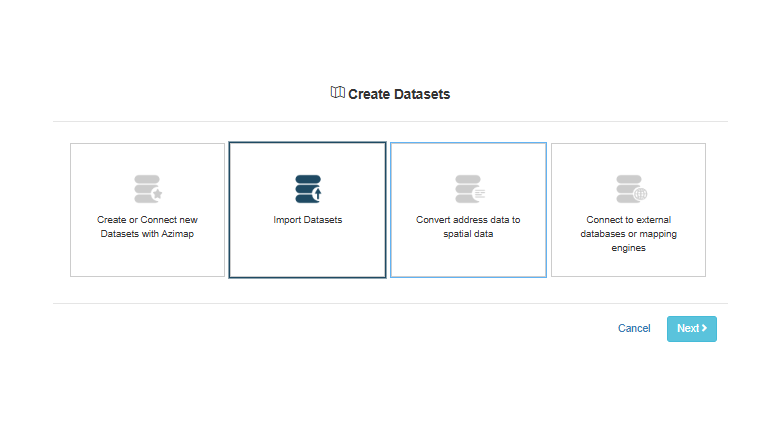
This will automatically bring you to
the first step of the CREATE DATASETS wizard.
Choose IMPORT DATASET.
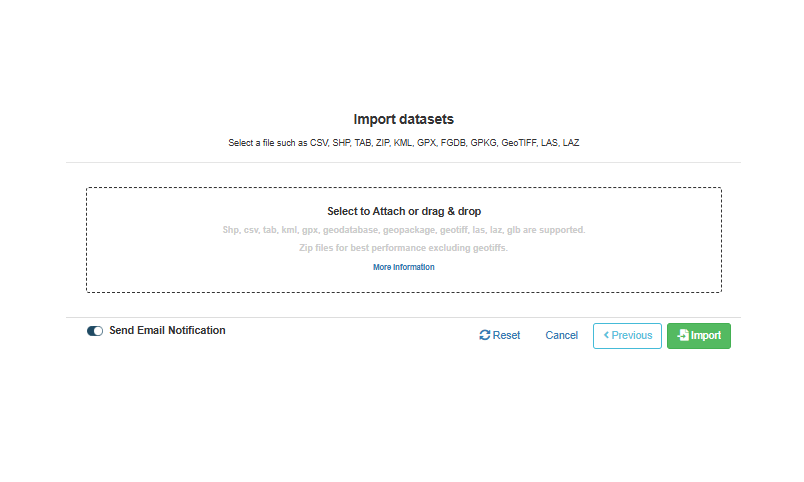
Drag and drop the earlier downloaded
zip file.
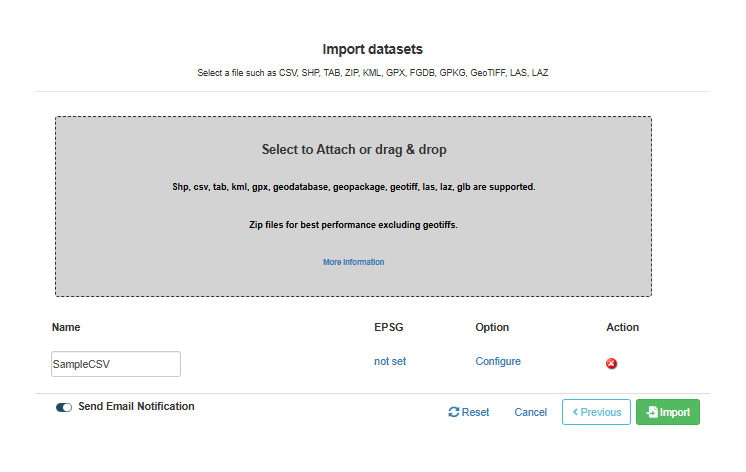
Rename your layers
after upload.
3. Configuring your imports
After upload, CSV
imports need to be configured.
3.1. Setting your coordinate system (EPSG)
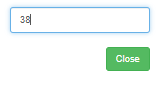
- Set EPSG code - All spatial data needs a co-ordinate system (this
is recognised automatically for spatial files like SHP or TAB but must be
set manually for CSV). Further
information on EPSG codes available here - For spatial
enabled CSV the correct coordinate system (EPSG) must be chosen or else
the data will be in the wrong location.
- Each country will have its own, or many of its own EPSG codes (GB:
27700, Ire: 2157)
- Searches can be processed by EPSG code or by name
- Latitude and longitude are in 'EPSG:4326' - worldwide coordinate
system in degrees
- Non-spatial CSV; can have any coordinate
system the user desires - let's choose 'EPSG: 4326' for it
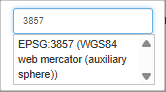
- Spatial CSV has a EPSG code of 'EPSG:3857' which
covers worldwide and is the same as our basemaps (Google, Bing,
OSM)
3.2. Configuration
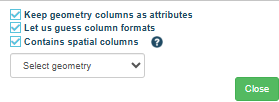
Under the OPTIONS section, click the CONFIGURE
button. You’ll be presented with the
following three options.
Here’s what they all mean:
KEEP GEOMETRY COLUMN AS ATTRIBUTES – this will
create a new column in with text version of the geometry (lat lon or Well Known
Text (WKT)) - useful for point features but a WKT of lines or polygons can be
very large
LET US GUESS COLUMN FORMATS - our importer
will try to auto discover the types in each column (string, text, date etc.). If unticked, all data will be imported as
string unless a .csvt file is used.
The .csvt file
has to have the same name as the .csv file it describes. It enables definition
of the following data types: Integer, Real, String, Date (YYYY-MM-DD), Time
(HH:MM:SS+nn) and DateTime (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS+nn) and geometry column
types (WKT, lat, X, lon, Y). A .csvt file contains only one line and the types
for each column need to be quoted and comma separated, e.g.
- Precision can also be applied
"Integer","Real","String(500)"
CONTAINS SPATIAL COLUMNS
Tick this if
you know that your CSV has a spatial (location data) column, e.g.
- CSV has a spatial column in WKT format
- Non Spatial CSV does not so this should be
unticked
- Supported column names are:
- WKT - short for Well Known Text. Details of format
available here. The type supports almost all geometry types including points,
lines, polygons, and their multi variants
- Lat or Y - lat of y for the Y axis point coordinate
- Lon or X - lon of x for the X axis point coordinate
SELECT GEOMETRY DROP DOWN
- Choose point, line or polygon
- For spatial CSV you must choose the format of the applicable type = point
- For non-spatial CSV you can choose the format you want to capture = line
Close and
click SAVE.
Your new
layers will be added to the map.
Thanks for
reading and if you haven't yet tried Azimap please go to the website to REGISTER.